
If you’ve ever used a Virtual Private Network (VPN) client on Windows 10 to connect to a private network, you might have noticed that your internet browsing slows down dramatically. I’ve been there myself, wondering why a feature designed for security and privacy is making my online experience feel sluggish.
The issue lies in how VPN connections work. When you connect to a VPN server, your device automatically adds a new default route for your network. This means all your web traffic (yes, every website you visit) is sent through the VPN connection and the remote private network instead of your local internet. While this setup can enhance security, it often comes at the cost of speed.
The solution to this problem is to implement “split tunneling,” a networking feature that allows you to maintain access to the private network while ensuring web traffic flows through your local internet connection. By enabling this feature, you can improve your browsing speeds while staying connected to the VPN.
In this guide, I’ll explain the steps to set up split tunneling on Windows 10 to fix a slow internet connection during a VPN session.
Fix VPN slow internet using split tunneling on Windows 10
To fix slow VPN connection on Windows 10, follow these steps:
-
Open Control Panel.
-
Click on Network and Internet.
-
Click on Network and Sharing Center.
-
Click the “Change adapter settings” option from the left pane.
-
Right-click the VPN connection adapter and select the Properties option.

-
Click the Networking tab.
-
Uncheck the “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)” option.
-
Check and select the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” option.
-
Click the Properties button.

-
Click the Advanced button.

-
Click the IP Settings tab.
-
Clear the “Use default gateway on remote network” option to enable split tunneling.
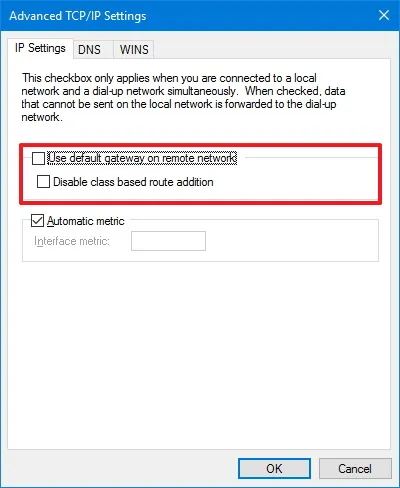
-
Click the OK button.
-
Click the OK button again.
-
Click OK one more time.
Once you complete the steps, you will have successfully configured split tunneling on Windows 10. This will enable your device to stay connected to two different networks simultaneously.
Considerations using split tunneling
It’s important to note that disabling the “Use default gateway on remote network” option comes with some considerations. While this setting allows access to the remote network, it only applies to the portion of the network that matches the network ID associated with the IP address you receive. This means that depending on your remote network requirements, you may want to consult with your network administrator to confirm these changes won’t affect your connection.
For many users, changing these settings makes sense because it prevents unnecessary web traffic from being routed through the VPN, which can slow down browsing speeds. However, the default behavior of routing all traffic through the VPN exists for security reasons. By directing all internet traffic through the VPN, organizations can enforce security measures such as firewalls, filters, and monitoring tools. This setup ensures compliance with corporate policies and offers a secure environment as if employees were physically connected to the network.
It’s also worth noting that the default settings are sufficient for most VPN users since they often interact with only one network at a time. Split tunneling is ideal for advanced use cases where simultaneous access to local and remote resources is necessary.
Although this guide focuses on Windows 10 and 11, the concept of split tunneling applies to other versions of Windows, including Windows 8.1 and Windows 7.
Other reasons for slow internet connection
Other factors can also contribute to slow internet speeds when using a VPN connection on Windows. For example, the distance of the VPN server can add latency and reduce speed. If the VPN server becomes overwhelmed with user traffic, it can lead to slower connections. Also, VPNs encrypt your data to enhance security, but this process requires more system resources and can slow down your connection, especially with high-level encryption protocols.
Some ISPs (Internet Service Providers) intentionally slow down VPN traffic, especially if they detect high bandwidth usage. Issues with your home network, such as weak Wi-Fi signals, outdated hardware, or bandwidth congestion, can reduce internet speeds. Some apps, such as streaming services, large downloads, or cloud sync tools, can compete for bandwidth, making your internet sluggish. Furthermore, the local firewall or antivirus settings can also impact speed performance.