- Windows 11 is secure by default, but you can further enhance protection in 2025 by enabling key features such as ransomware and phishing protection, Smart App Control, Core Isolation, and BitLocker encryption. Regular updates, virus scans, and switching to a standard account further reduce risks. For added privacy, enable DNS over HTTPS, Windows Sandbox, and random MAC addresses.
UPDATED 9/5/2025: Although Windows 11 is the most secure version of the operating system, you can still add some custom configurations and follow best practices to improve the security of your device.
As part of the best security practices, you can check for system updates and scan the computer for viruses. You can also configure security features, such as ransomware and phishing protection, firewall, biometric authentication, encryption, and other most sonicated features like Smart App Control and Core Isolation.
If you need to install an application from an untrusted source, you can use Windows Sandbox to create a lightweight virtual machine for testing the application without risking the main installation.
In this guide, I’ll outline a collection of the best security settings for Windows 11 in 2025.
Windows 11 best security settings to change in 2025
These are the best security settings to enable, configure, or disable on Windows 11. (You don’t have to configure every one of them. You should only use the ones you consider the best for your situation.)
1. Install system updates
On Windows 11, installing the latest updates is one of the best ways to keep your device and files secure since updates can fix bugs, enhance security, and improve system performance.
To install Windows 11 updates manually, use these steps:
-
Open Settings on Windows 11.
-
Click on Windows Update.
-
Click the Check for updates button.

-
(Optional) Turn on the “Get the latest updates as soon as they’re available” toggle switch.
-
Click the “Download and install” button to apply a preview of an upcoming update (if applicable).
Quick note: Optional updates usually include non-security changes that Microsoft plans to release in the next Patch Tuesday rollout. -
Click the Restart now button.
Once you complete the steps, if an update is available, it will download and install automatically on Windows 11.
In addition to using the Windows Update settings, you can update the system through different methods, such as Command Prompt, PowerShell, and the Microsoft Update Catalog website.
1. Scan computer for viruses
Windows 11 includes Microsoft Defender Antivirus to detect and remove virtually all malware, including viruses, ransomware, spyware, and rootkits. If you suspect your computer has been compromised, run a full or offline scan (especially for severe infections) to ensure your device is malware-free. Even with third-party antivirus software, periodic scanning is a good security practice.
Full virus scan
To perform a full virus scan on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
-
Click on Virus & threat protection.
-
Click on Scan options under the “Current threats” section.

-
Select the Full scan option to check the entire system for viruses and any other type of malware.

-
Click the Scan now button.
After you complete the steps, Microsoft Defender Antivirus will scan the computer for malware. If anything is detected, the anti-malware automatically removes (or quarantines) the threats.
You can also use the antivirus with Command Prompt and PowerShell.
Offline virus scan
To run an offline virus scan on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Virus & threat protection.
-
Click on Scan options under the “Current threats” section.

-
Check the “Microsoft Defender Offline scan” option.

-
Click the Scan now button.
-
Click the Scan button.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will restart automatically in the recovery environment, and Microsoft Defender will start the full virus scan. If the Windows 11 antivirus detects any virus, rootkit, or other type of malware, it automatically removes it.
Enable periodic scanning
If you have another antivirus solution, another best security practice is to enable “periodic scanning” on Windows 11, a feature that periodically scans and removes threats that other antivirus software may have missed.
To enable “periodic scanning” on Microsoft Defender Antivirus for Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Virus & threat protection.
-
Click the “Microsoft Defender Antivirus options” setting.
-
Turn on the Periodic scanning toggle switch.

After you complete the steps, the Windows 11 antivirus will use the “Automatic Maintenance” feature to run the scans at optimal times to minimize the impact on performance and battery life.
3. Enable ransomware protection
Windows 11’s “Controlled folder access” is another best built-in security feature designed to protect your computer from ransomware attacks. It monitors application file changes. If a blacklisted app attempts to modify files in a protected folder, the system notifies you of the suspicious activity.
To enable the Controlled folder access anti-ransomware protection on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Virus & threat protection.
-
Click the “Manage ransomware protection” setting under the “Ransomware protection” section.

-
Turn on the “Controlled folder access” toggle switch.

Once you complete the steps, Microsoft Defender Antivirus will monitor the protected folders as applications try to modify your files. If suspicious activity occurs, you’ll get a notification about the threat.
In addition to enabling the feature, it is half of the equation. You can always use these instructions to prevent the feature from blocking trusted applications and protect folder locations other than the defaults.
4. Enable phishing protection
Windows 11 offers Enhanced Phishing Protection through Microsoft Defender SmartScreen, safeguarding your passwords from malicious sites and applications. This feature operates in three key ways:
- Warning on Untrusted Sites or Apps: It alerts you when you enter your account password on untrusted websites or applications.
- Plain Text Password Alerts: It notifies you if you attempt to save passwords in plain text within any application.
- Password Reuse Notifications: It cautions against reusing passwords across different accounts, a practice that can make it easier for hackers to compromise your information.
This protection applies to Microsoft accounts, local accounts, Active Directory, and Azure Active Directory. However, it functions only when using a password. As a result, Windows Hello must be disabled to enable phishing protection.
I would only recommend this feature if required or if you are already not using Windows Hello. Otherwise, you will probably be better off using passkeys (see instructions below).
To enable phishing protection on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click the Sign-in options tab.
-
Turn off the “For improved security, only allow Windows Hello sign-in for Microsoft accounts on this device” toggle switch under the “Additional settings” section.

-
Select the active Windows Hello option (facial recognition, fingerprint recognition, or PIN) under the “Ways to sign in” section.
-
Click the Remove button.
-
Click the Remove button again.
-
Confirm your Microsoft account password.
-
Click the OK button.
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on App & browser control.
-
Click the “Reputation-based protection settings” option.

-
Turn on the “Phishing protection” toggle switch to enable the security feature.

-
Check the “Warm me about malicious apps and sites” option to display a warning when on an untrusted website or program.
-
Check the “Warm me about password reuse” option to avoid using the same password when creating a new account or updating the information on a website or program.
-
Check the “Warm me about unsafe password storage” option to warn you not to save a password in plain text in a text editor.
Once you complete the steps, the “Enhanced Phishing Protection” feature will warn you when entering a password on an untrusted app or website with the option to change the password to reduce the chances of someone gaining unauthorized access to your account.
Since text editors or Office apps were not designed to protect your credentials, you will also get a warning when trying to reuse a password or save passwords in these applications.
5. Create passkeys for websites and apps
Passkeys offer a secure and convenient alternative to traditional passwords for signing into websites and applications that support this authentication method. Instead of relying on passwords, passkeys utilize public key cryptography, creating a unique cryptographic key pair associated with your account. This key pair is securely stored on your Windows 11 device. When accessing the service again, you’ll use Windows Hello (employing biometrics like facial recognition, fingerprint, or a PIN) to authenticate, eliminating the need for a password.
This approach improves security by removing passwords from the sign-in process, making it significantly more challenging for hackers to compromise your accounts. Passkeys are part of a broader security standard adopted by major companies, including Microsoft, Google, Apple, Amazon, and PayPal, aiming to provide a unified and secure authentication experience across platforms.
To create a passkey, navigate to the account security settings of a supported service or application and follow the prompts to set up passkey authentication. Once configured, your passkeys can sync across devices using your Microsoft account, allowing seamless access on any Windows 11 device. Some online services may even offer to set up a passkey during the sign-in process.
The following example creates a passkey for your Google account:
-
Open Microsoft Edge (or Google Chrome).
-
Open your Google Account.
-
Sign in and open the web service account settings.
-
Turn on the “Passkey sign-in” option.
-
Click the “Create a Passkey” option.

-
Click the Continue button.

-
Confirm your account credentials on Windows Hello.

-
Click the OK button.
-
Click the Done button.
Once you complete the steps, the passkey will be downloaded as a token on your computer. The next time you want to access the service (or app), you can use Windows Hello authentication to complete the sign-in process instead of using the service password.
The token is only valid per device, meaning you must create a passkey on every device you want to access the service. You can view and delete passkeys from Settings > Account > Passkeys.
6. Check firewall settings
The Microsoft Defender Firewall can monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic to allow or block connections based on predefined rules to protect your computer and information from unauthorized access. The feature should be enabled by default, but it’s always a good idea to check and enable it if it’s not.
To enable the firewall through Windows Security, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on Firewall & network protection.
-
Click the active network option.

-
Turn on the “Microsoft Defender Firewall” toggle switch to turn off the firewall.

After you complete the steps, the firewall will turn on for the active network profile.
7. Enable DNS over HTTPS (DoH)
If you want an extra layer of security and privacy when surfing the internet, you must enable DNS over HTTPS (DoH).
DNS over HTTPS is a networking protocol designed to encrypt Domain Name System (DNS) queries using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) protocol, thereby enhancing privacy and minimizing attacks from hackers that can view and manipulate DNS traffic.
Some applications like Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox already support this feature, but you can also configure it on Windows 11. Here’s how:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Network & internet.
-
Click the Ethernet or Wi-Fi tab (depending on the active connection).
Quick note: If you have a Wi-Fi connection, click on the connection properties to access the settings. -
Click the Edit button from the “DNS server assignment” setting.

-
Select the Manual option from the drop-down menu.
-
Turn on the IPv4 toggle switch.
-
Under the “Preferred DNS” and “Alternate DNS” sections, specify the primary and secondary DoH IP address from one of the supported services. For example, you can use Cloudflare (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) or Google (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4)

-
Use the “DNS over HTTPS” drop-down menu and select the On (automatic template) option since it sends all DNS traffic with encryption, but you can also choose other encryption preferences.
-
Turn off the “Fallback to plaintext” toggle switch.
Quick tip: If you enable this feature, the system will encrypt DNS traffic, but it allows queries to be sent without encryption. -
Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will encrypt DNS traffic over the HTTPS protocol for a more secure and private experience.
You can learn more details and how to confirm the DoH settings are working with these instructions.
8. Enable Windows Hello Face or fingerprint
As part of the best security settings for Windows 11, you can also use Windows Hello, which allows you to increase your computer’s security by adding biometric elements (such as your face or fingerprint) to sign in to your profile. If you don’t have a device that integrates some biometric hardware, you must purchase a compatible face recognition camera or fingerprint reader to set it up.
Enable face recognition authentication
To configure Windows Hello facial recognition to unlock a computer on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click the Sign-in options page on the right side.
-
Select the “Facial recognition (Windows Hello)” setting under the “Ways to sign in” section.
-
Click the Set up button.

-
Click the Get started button.

-
Confirm your current password (or PIN).
-
Look directly into the camera for Windows 11 to create a facial recognition profile of your face.

-
Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, you can lock your computer (Windows key + L) and look into the camera to sign in.
Enable fingerprint authentication
To set up Windows Hello with a fingerprint reader, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click on Sign-in options.
-
Select the “Fingerprint recognition” setting under the “Ways to sign in” section.
-
Click the Set up button to enable the Windows Hello fingerprint option.

-
Click the Get started button.

-
Confirm your account password.
-
Touch the fingerprint sensor as indicated in the wizard.

-
Continue with the on-screen directions to capture your fingerprint from various angles.
After completing the steps, you can lock your device and use the fingerprint reader to sign in with your finger.
9. Enable Dynamic Lock
Dynamic Lock is a security feature built into Windows 11 that locks your computer when you step away, based on the proximity of a Bluetooth-paired device (such as your phone or wearable), adding an extra layer of security.
To enable Dynamic Lock on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Turn on the peripheral.
-
Turn on the device’s Bluetooth pairing option to make it discoverable.
-
Open Settings on Windows 11.
-
Click on Bluetooth & devices.
-
Turn on the Bluetooth toggle switch to enable the wireless radio (if applicable).
-
Click the Add device button.

-
Select the Bluetooth option.

-
Choose the Bluetooth device from the list.

-
Continue with the on-screen directions (if applicable).
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click the Sign-in options tab.
-
Select the Dynamic lock setting.
-
Check the “Allow Windows to automatically lock your device when you’re away” option.

Once you complete the steps, when the Bluetooth device isn’t near the computer, Windows 11 will turn off the screen and lock your account after 30 seconds of inactivity.
10. Block unwanted apps
Windows Security has a feature to protect your installation against malicious apps. The feature is known as “reputation-based protection,” it can detect and block low-reputation apps that may cause unexpected behaviors on Windows 11, such as poorly designed or harmful apps.
To enable reputation-based protection to protect Windows 11 from unwanted apps, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on App & browse control.
-
Click the “Reputation-based protection settings” option under the “Reputation-based protection” section.

-
Turn on the “Potentially unwanted app blocking” toggle switch.

-
Check the Block apps option.
-
Check the Block downloads option.
After completing the steps, Windows 11 can detect and block apps with a low reputation that may cause issues.
11. Enable encryption
BitLocker is yet another feature on the list that can be considered one of the best for security, as it allows you to use encryption on a drive to protect your data from unauthorized access to your documents, pictures, and any other data stored on the computer.
The feature is only available in the Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions of Windows 11. However, on Windows 11 Home, you can use “device encryption” on some devices.
It’s important to note that starting with the release of Windows 11 24H2 and subsequent releases, the system will automatically enable device encryption on new installations.
Enable device encryption on Windows 11 Pro
To configure BitLocker on a Windows 11 drive, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Storage.
-
Click on Advanced storage settings under the “Storage management” section.
-
Click on Disks & volumes.

-
Select the drive with the volume to encrypt.
-
Choose the volume to enable BitLocker encryption and click the Properties button.

-
Click the “Turn on BitLocker” option.

-
Click the “Turn on BitLocker” option under the “Operating system drive” section.

-
Select the “Save to your Microsoft account” option (recommended).

-
Click the Next button.
-
Select the “Encrypt used disk space only” option.

-
Click the Next button.
-
Select the “New encryption mode” option.

-
Click the Next button.
-
Check the “Run BitLocker system check” option.

-
Click the Restart now button.
After you complete the steps, the computer will restart to apply the encryption settings and enable BitLocker.
You can also enable encryption for secondary and external drives. And using BitLocker To Go, you can protect your data on USB flash drives.
Enable device encryption on Windows 11 Home
To configure BitLocker encryption on Windows 11 Home, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Privacy & Security.
-
Click the Device encryption page under the “Security” section.

-
Turn on Device encryption to enable BitLocker on Windows 11 Home.

Once you complete the steps, the feature will encrypt the entire system drive.
If you no longer need encryption, it’s possible to decrypt the drive using the same instructions.
12. Enable Smart App Control
On Windows 11, Smart App Control (SAC) is a security feature that locks the system down, allowing it to run only trusted apps or apps with valid certificates to prevent unwanted behaviors from untrusted applications.
To enable Smart App Control on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Windows Security.
-
Click on App & browse control.
-
Click on Smart App Control settings.

-
Select the Evaluation option.

After you complete the steps, the feature will run quietly in the background but not block anything. However, in this stage, the system will learn from your applications to determine whether the feature can run without affecting the experience.
If Smart App Control can run as expected, the system will turn it on automatically. If the feature gets in the way, the system will automatically turn it off.
Once the evaluation is complete, the feature will enable automatically, but you won’t be able to turn it off. Additionally, if the system blocks an app, you won’t be able to unblock it unless you disable the feature, which will require a complete reinstallation of the operating system.
13. Enable Core Isolation
Core Isolation is a collection of security features that protect your computer from malicious code and hackers. One of the features available is memory integrity, which blocks different types of malware from compromising high-security processes in memory.
The feature should be enabled by default on Windows 11, but if it’s not, you can use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
-
Click on Device Security.
-
Click the “Core isolation details” option under the “Core isolation” section.

-
Turn on the “Memory integrity” toggle switch to enable the Core isolation.

-
Restart the computer.
Once you complete the steps, the security feature will be enabled on Windows 11.
14. Windows Sandbox
The Windows Sandbox feature provides a full desktop virtualization experience for installing and testing untrusted applications, isolated from the main installation.
To enable Windows Sandbox on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on System.
-
Click the Optional features page.

-
Click the “More Windows features” setting under the “Related settings” section.

-
Check the Windows Sandbox option.

-
Click the OK button.
-
Click the Restart now button.
Once you complete the steps, you can run Windows Sandbox from the Start menu.

If you need to install an application, you can download the installer from the internet using the browser available on the virtual machine or from the main installation. Then, copy and paste the file onto the Windows Sandbox desktop and install it in the isolated environment.
15. Full backup
On Windows 11, a full backup is one of the best security practices to create a copy of the entire system. This allows you to recover in case of critical system problems, malware attacks like ransomware, hardware failure, or upgrading the primary drive. In addition, a backup can help you roll back to a previous installation after upgrading to a new feature update or hard drive.
You can always choose a third-party solution, but you can still use the (deprecated) legacy “System Image Backup” tool to save a full backup to a USB hard drive.
To create a full backup on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Control Panel and click the top result to open the app.
-
Click on System and Security.
-
Click on File History.
-
Click the “System Image Backup” option from the left pane.

-
Click the “Create a system image” option from the left pane.

-
Select the external drive to save the Windows 11 backup.

-
Click the Next button.
-
Click the Start backup button.

-
Click the No button.
-
Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, Windows 11 will create a full computer backup.
You will also receive the option to create a repair disk, but you can ignore it since you can use the Windows 11 bootable media to access the recovery settings to restore the backup.
In addition to periodically backing up your device, it’s recommended that you store your files in the cloud using third-party services like OneDrive. This approach will protect the files from hardware failure, ransomware, or theft.
Alternatively, copying your files to an external drive with a simple copy and paste (as long as you don’t have a lot of data) is another way to protect your documents, pictures, videos, and other files.
16. Switch from Administrator to Standard User account
Windows 11 offers two account types, including Administrator and Standard User, each with different permission levels. The Administrator type has full system access, enabling them to change settings, run elevated tasks, and perform any action. The Standard User type operates in a more restricted environment, able to use existing applications but unable to install new ones or modify system-wide settings.
Since using an account without restrictions can be a security risk, switching to a standard account is one of the best practices to improve security. You can create a new “Administrator” account only for management and change your account type to “Standard User.”
Create local administrator account
To create an administrator local account through the Settings app, use these steps:
-
Open Start.
-
Search for Settings and click the top result to open the app.
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click the Other users page.
-
Click the Add account button under the “Other users” section.

-
Click the “I don’t have this person’s sign-in information” option.

-
Click the “Add a user without a Microsoft account” option.

-
Create an administrator account by confirming a name and password.

-
Create security questions and answers to recover your account if you lose your password.
-
Click the Next button.
-
Select the newly created account and click the “Change account type” button.

-
Select the Administrator option from the “Account type” setting.

-
Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the new account will appear on your Windows 11 device.
Switch to standard account
To change an “Administrator” account to a “Standard Users” account on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Sign out of your current account.
-
Sign in to the newly created administrator account.
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Accounts.
-
Click the Other users page.
-
Select the primary account.
-
Click the “Change account type” button.

-
Select the Standard User option from the “Account type” setting.

-
Click the OK button.
After completing the steps, the original account will switch from “Administrator” to “Standard User” account type. You will be prompted to confirm the administrator credentials to make system changes or install new apps. You can still sign in to the administrator account to perform system changes.
17. Disable Remote Desktop
Although the Remote Desktop feature allows you to access files and apps from another location or offer assistance without being present at the site, it also presents a security risk. It may help a malicious individual gain unauthorized access to the computer. As a best security practice, turn off the feature if you don’t use it.
To disable Remote Desktop on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on System.
-
Click on Remote Desktop.
-
Turn off the Remote Desktop toggle switch.

-
Click the Confirm button.
Once you complete the steps, malicious individuals should no longer be able to exploit the RDP protocol to gain unauthorized access to your computer.
18. Sync time and date
On Windows 11, it’s also important to keep the system time and date correct. Otherwise, it could cause security problems, such as trying to sign in to a service or application on the network or the internet.
To update the time and date on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Time & language.
-
Click the Date & time page.
-
Turn on the “Set time automatically” toggle switch.
-
Click the Sync now button under the “Additional settings” section.

After completing the steps, Windows 11 will update and display the correct time on your computer.
19. Create system restore point
System Restore allows you to create a copy of the system state as a “restore point” to protect the hard drive’s data if something goes wrong after an update, when installing an application, or when making system changes. The feature automatically creates a restore point when it detects system changes (such as installing a new update or driver), but you can always make a restore point manually.
To create a restore point on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Start on Windows 11.
-
Search for Create a restore point and click the top result to open the app.
-
Select the system drive (C) and click the Configure button under the “Protection Settings” section.

-
Select the “Turn on system protection” option.

-
Click the Apply button.
-
Click the OK button.
-
Click the Create button to create a restore point on Windows 11.

-
Confirm a name for the restore point.
-
Click the Create button.
-
Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, the system will create a restore point that includes system files, installed applications, system settings, and a backup of the Registry.
You can also follow these instructions to restore the device using a restore point. If the restoration doesn’t work, you may need to reset the system.
20. Disable Windows Recall
Windows Recall is a new AI feature designed to give your computer a “photographic memory” by taking snapshots of your screen every few seconds and then using AI to make that data searchable.
Although this feature can make it convenient to retrace your steps and find virtually anything you have seen or done in the past, it also raises significant privacy concerns, as it essentially records everything you do on your computer.
Storing all this data could make your computer a more attractive target for hackers, and taking and analyzing snapshots could impact system performance.
If you have a Copilot+ PC, you can reset and disable Recall on Windows 11 by following a few simple steps.
To completely disable Recall on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Privacy & security.
-
Click the Recall & snapshots page.
-
Click on Advanced settings.

-
Click the Reset Recall button.

-
Click the Reset button.
After completing these steps, Windows 11 will delete all collected snapshots, filters for apps and websites, restore all settings for Recall to their original defaults, and disables the feature.
You can also uninstall the Recall feature from the operating system if you’re still concerned about the security and privacy of your device and data.
21. Enable random MAC address
Laptops and other computers equipped with Wi-Fi adapters are constantly scanning for networks, broadcasting their MAC addresses, which can be used to track their locations. MAC address randomization (using random hardware addresses) enhances privacy by regularly changing this address, making it more difficult to track.
To enable random hardware addresses for all wireless networks, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on Network & internet.
-
Click the Wi-Fi page.
-
Turn on the “Random hardware addresses” toggle switch to enable the feature.
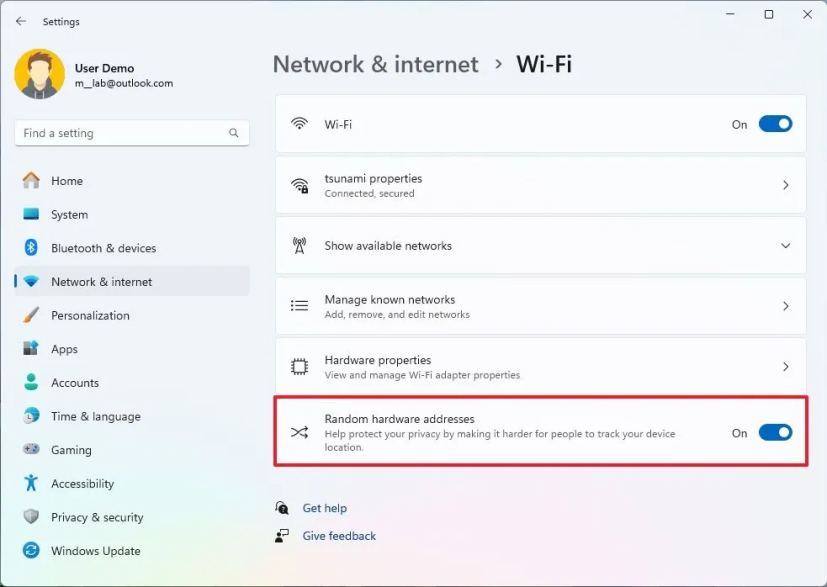
-
(Optional) Turn off the “Random hardware addresses” toggle switch to disable the feature.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will use a random hardware address to scan for networks and connect to any access point.
It’s also possible to enable random hardware addresses on a specific network.
22. Enable Scareware Blocker on Microsoft Edge
On Microsoft Edge, the Scareware Blocker is a security feature that uses AI to protect you from online scams, particularly those known as “scareware.”
The feature has been trained to identify the telltale signs of scareware scams, such as:
- Full-screen pop-ups that are hard to close.
- Messages claiming your computer is infected.
- Urgent calls to action to contact fake “tech support.”
- Web page design mimicking official system warnings.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on known threats, Scareware Blocker uses AI to spot new and evolving scams in real time.
It’s important to note that Windows 11 and Microsoft Edge also implement the Defender SmartScreen feature, a similar technology that protects you from phishing, online threats, and different types of malware. However, this feature relies on a cloud-based database to detect threats, which can take some time to update. The Scareware Blocker analyzes the screen using AI to determine if the page is legit or a threat without the need for a database.
In other words, the Scareware Blocker is an extra layer of protection to complement the Defender SmartScreen feature.
To enable Scareware Blocker on Microsoft Edge, use these steps:
-
Open Microsoft Edge.
-
Click the “Settings and more” button in the top-right.
-
Click the Settings option.
-
Click on “Privacy, search, and services” from the left pane.
-
Click the Security page.
-
Turn on the Scareware blocker toggle switch under the “Security” section

-
Turn on the “Microsoft Defender SmartScreen” toggle switch (if applicable).
After completing the steps, the Scareware Blocker security feature will be enabled, and you’ll receive a warning if the system detects scareware on the screen, with the option to block or continue if it’s a false positive.

23. Enable Presence Sensing
On Windows 11, Presence Sensing is a collection of features that can improve the device security and energy efficiency of your computer.
The feature requires specialized hardware, such as infrared cameras or radar-based sensors, to detect when a person is near or far from a device.
This feature is usually found on premium computers and Copilot+ PCs. If your device does not have compatible presence sensors, you won’t find any options in the Settings app.
On supported hardware, the computer can automatically turn off the display when you leave and turn it back on when you return. It can also dim the screen when you look away and brighten it when you look back. This feature enhances security, saves battery, and improves workflow.
To configure the Presence Sensing settings on Windows 11, use these steps:
-
Open Settings.
-
Click on System.
-
Click the Power & battery tab.
-
Click on the “Screen, sleep, & hibernate timeouts” setting.
-
Turn on the “Turn off my screen when I leave” toggle switch to allow the system to turn off the display as you walk away.

-
Turn on the “Wake up my device when I approach” toggle to allow the system to turn on the display as soon as it detects your presence.
-
Turn on the “Dim my screen when I look away” toggle switch to allow the operating system to lower the brightness intensity when you are not looking at the screen.
-
Click any of the settings (from steps 5, 6, or 7) to open the Presence Sensing settings page.
-
Click the “Turn off my screen when I leave” setting.

-
Choose the number of feet the feature should use to determine the distance when you have left your computer in the “Consider me gone when I’m this far away” setting.
-
Choose the time to wait before your screen turns off after you have left your computer in the “Then, turn off my screen after this amount of time” setting.
Quick note: When the screen turns off, the system will also lock the device, meaning that you will need to sign in again to resume your session. -
Check the”Turn off my screen when I leave while an external display is connected” option (if applicable).
-
Click the “Wake my device when I approach” setting.
-
Choose the number of feet the feature should use to determine how close you need to be for your computer to wake when you approach it in the “Wake my device when I’m this close” setting.
-
Check the “Wake my device when I approach while an external display is connected” option (if applicable).
-
Click the “Dim my screen when I look away” setting.

-
Check the “Dim my screen when I look away while an external display is connected” option (if applicable).
Once you complete the steps, the system will control the desktop access, screen, and sleep timers, depending on your configuration.
You can also control the Presence Sensing privacy settings from the “Privacy & Security” settings.
What security settings are you changing on Windows 11? Let me know in the comments.
Update September 5, 2025: This guide has been updated to ensure accuracy and reflect changes to the process.
